Interactive work on the compute nodes
Learning objectives
Understand what an interactive session is
Understand why one may need an interactive session
How to work with an interactive session (single + multiple cores)
Run an interactive-friendly Python script
Run an interactive-unfriendly Python script
- How to load IDEs
Jupyter
VScode
spyder
On-demand desktop
Questions
- Imagine you are developing a Python script in a line-by-line fashion. How to do so best?
Why not do so on the login node?
Why not do so by using
sbatch?
What is the drawback of using an interactive node?
Compute allocations in this workshop
Rackham:
naiss2024-22-1442Kebnekaise:
hpc2n2024-142Cosmos:
lu2024-2-88Tetralith:
naiss2024-22-1493
Storage space for this workshop
Rackham:
/proj/hpc-python-fallKebnekaise:
/proj/nobackup/hpc-python-fall-hpc2nCosmos:
/lunarc/nobackup/projects/lu2024-17-44Tetralith:
/proj/hpc-python-fall-nsc
Reservation
Include with #SBATCH --reservation==<reservation-name>. On UPPMAX it is “magnetic” and so follows the project ID without you having to add the reservation name.
NOTE as there is only one/a few nodes reserved, you should NOT use the reservations for long jobs as this will block their use for everyone else. Using them for short test jobs is what they are for.
- UPPMAX
naiss2024-22-1442_1 for cpu on Thursday
naiss2024-22-1442_2 for gpu on Thursday
naiss2024-22-1442_3 for cpu on Friday
naiss2024-22-1442_4 for gpu on Friday
- HPC2N
hpc-python-cpu-th for cpu on Thursday
hpc-python-gpu-th for gpu on Thursday
hpc-python-cpu-fr for cpu on Friday
hpc-python-gpu-fr for gpu on Friday
Introduction
Some users develop Python code in a line-by-line fashion.
These users typically want to run a (calculation-heavy) script frequently, to test if the code works.
However, scheduling each new line is too slow, as it can take minutes (or sometimes hours) before the new code is run.
Instead, there is a way to directly work with such code: use an interactive session.
Some other users want to run programs that (1) use a lot of CPU and memory, and (2) need to be persistent/available. One good example is Jupyter.
Running such a program on a login nodes would harm all other users on the login node.
Running such a program on a computer node using
sbatchwould not allow a user to connect to it.In such a case: use an interactive session.
About Jupyter
For HPC2N, using Jupyter on HPC2N is possible, through a batch job.
For UPPMAX, using Jupyter is easier.
For LUNARC, using Jupyter (<https://lunarc-documentation.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guides/applications/Python/#jupyter-lab>) works best using the LUNARC HPC Desktop. Go to the Applications menu, hover over Applications - Python, and select Jupyter Lab from the menu that pops up to the right.
For NSC, using Jupyter is easiest done through ThinLinc, but can also be used via an SSH tunnel.
In this session we will talk about
interactive/salloc
Jupyter
VScode
Spyder
Open-on-demand desktop
An interactive session is a session with direct access to a compute node. Or alternatively: an interactive session is a session, in which there is no queue before a command is run on a compute node.
The different way HPC2N, UPPMAX, LUNARC, and NSC provide for an interactive session
Example, HPC2N vs. UPPMAX vs. LUNARC (NSC is similar to LUNARC):
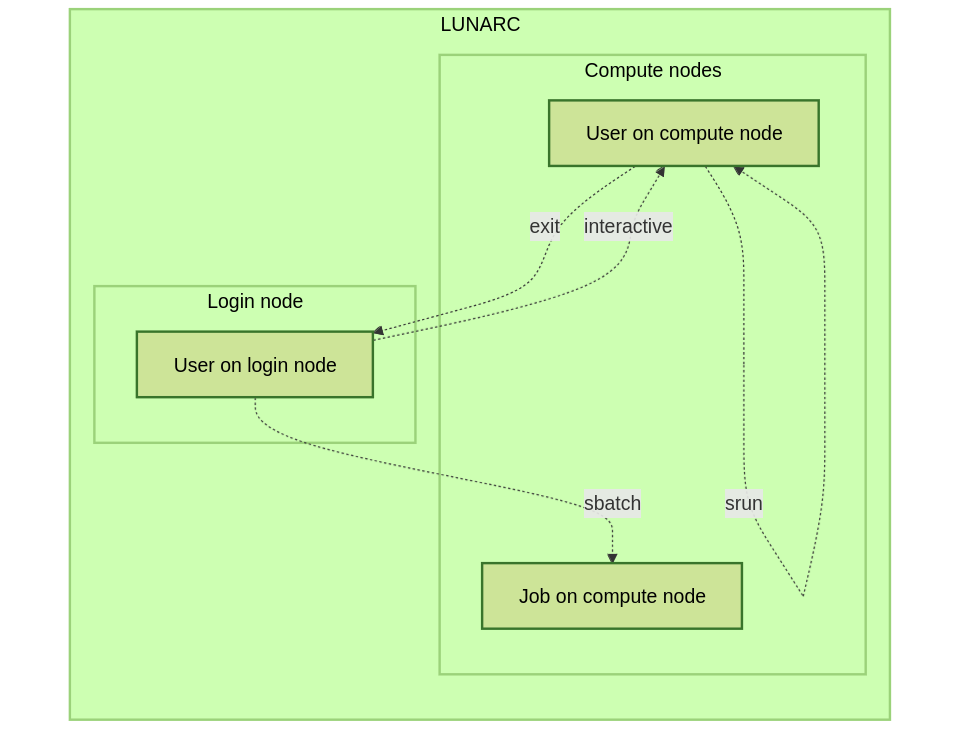
Here we define an interactive session as a session with direct access to a compute node. Or alternatively: an interactive session is a session, in which there is no queue before a command is run on a compute node.
This differs between HPC2N and UPPMAX :
HPC2N: the user remains on a login node. All commands can be sent directly to the compute node using
srunUPPMAX: the user is actually on a computer node. Whatever command is done, it is run on the compute node
LUNARC: the user is actually on a computer node if the correct menu option is chosen. Whatever command is done, it is run on the compute node
NSC: the user is actually on a computer node if the correct menu option is chosen. Whatever command is done, it is run on the compute node
Start an interactive session
To start an interactive session, one needs to allocate resources on the cluster first.
The command to request an interactive node differs per HPC cluster:
Cluster |
|
|
GfxLauncher |
|---|---|---|---|
HPC2N |
Works |
Recommended |
N/A |
UPPMAX |
Recommended |
Works |
N/A |
LUNARC |
Works |
N/A |
Recommended |
NSC |
Recommended |
N/A |
N/A |
Start an interactive session in the simplest way
To start an interactive session in the simplest way, is shown here:
Use:
interactive -A [project_name]
Where [project_name] is the UPPMAX project name,
for example interactive -A naiss2024-22-1442.
The output will look similar to this:
[richel@rackham4 ~]$ interactive -A naiss2024-22-1442
You receive the high interactive priority.
You may run for at most one hour.
Your job has been put into the devcore partition and is expected to start at once.
(Please remember, you may not simultaneously have more than one devel/devcore job, running or queued, in the batch system.)
Please, use no more than 8 GB of RAM.
salloc: Pending job allocation 9093699
salloc: job 9093699 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 9093699 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 9093699
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes r314 are ready for job
_ _ ____ ____ __ __ _ __ __
| | | | _ \| _ \| \/ | / \ \ \/ / | System: r314
| | | | |_) | |_) | |\/| | / _ \ \ / | User: richel
| |_| | __/| __/| | | |/ ___ \ / \ |
\___/|_| |_| |_| |_/_/ \_\/_/\_\ |
###############################################################################
User Guides: https://docs.uppmax.uu.se/
Write to support@uppmax.uu.se, if you have questions or comments.
[richel@r314 ~]$
Note that the prompt has changed to show that one is on an interactive node.
salloc -A [project_name]
Where [project_name] is the HPC2N project name,
for example salloc -A hpc2n2024-142.
This will look similar to this (including asking for resources - time is required):
b-an01 [~]$ salloc -n 4 --time=00:10:00 -A hpc2n2024-142
salloc: Pending job allocation 20174806
salloc: job 20174806 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 20174806 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 20174806
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes b-cn0241 are ready for job
b-an01 [~]$ module load GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3
b-an01 [~]$
interactive -A [project_name]
Where [project_name] is the LUNARC project name,
for example interactive -A lu2024-2-88.
This will look similar to this (including asking for resources - time is required):
[bbrydsoe@cosmos3 ~]$ interactive -A lu2024-2-88 -n 4 -t 00:10:00
Cluster name: COSMOS
Waiting for JOBID 988025 to start
The terminal will refresh for the new connection:
[bbrydsoe@cn137 ~]$ module load GCC/13.2.0 Python/3.11.5
[bbrydsoe@cn137 ~]$
interactive -A [project_name]
Where [project_name] is the NSC project name,
for example interactive -A naiss2024-22-1493.
This will look similar to this:
[x_birbr@tetralith1 ~]$ interactive -A naiss2024-22-1493
salloc: Pending job allocation 40137281
salloc: job 40137281 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 40137281 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 40137281
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes n302 are ready for job
[x_birbr@n302 ~]$ module load buildtool-easybuild/4.8.0-hpce082752a2 GCC/13.2.0 Python/3.11.5
[x_birbr@n302 ~]$
Indeed, all you need is the UPPMAX/NSC project name, as well as time for HPC2N/LUNARC.
However, this simplest way may have some defaults settings that do not fit you.
session duration is too short
the session has too few cores available
You can add more resources the same way as for batch jobs.
There is some information here: <https://uppmax.github.io/R-python-julia-matlab-HPC/python/interactivePython.html#start-an-interactive-session-in-a-more-elaborate-way>.
End an interactive session
You leave interactive mode with exit.
Check to be in an interactive session
For UPPMAX, LUNARC, and NSC
You check if you are in an interactive session with:
hostname
If the output contains the words rackham, cosmos, or tetralith you are on the login node.
If the output contains:
r[number].uppmax.uu.se, where[number]is a number, you are on a compute node at UPPMAX (rackham).cn[number], where[number]is a number, you are on a compute node at LUNARC (cosmos).n[number], where[number]is a number, you are on a compute node at NSC (tetralith).
For HPC2N
You check if you are in an interactive session with:
srun hostname
If the output is
b-cn[number].hpc2n.umu.se, where[number]is a number, you are more-or-less on a compute node.If the output is
b-an[number], where[number]is a number, you are still on a login node.
Do NOT do
hostname
for HPC2n as it will always show that you are on a login node
Check that the number of cores booked is correct
You can do this with
$ srun hostname
And then you will get one line of output per core booked.
Running a Python script in an interactive session
To run a Python script in an interactive session, first load the Python modules:
module load [python/version + any prerequisites]
To run a Python script on 1 core, do:
python [my_script.py]
where [my_script.py] is the Python script (including the path if it is ot in the current directory), for example srun python ~/my_script.py.
To run a Python script on each of the requested cores, do:
srun python [my_script.py]
where [my_script.py] is the Python script (including the path if it is noth in the current directory), for example srun python ~/my_script.py.
To run a Python script in an interactive session, first load the Python modules + prerequisites:
module load GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3
To run a Python script on each of the requested cores, do:
srun python [my_script.py]
where [my_script.py] is the Python script (including the path if it is noth in the current directory), for example srun python ~/my_script.py.
Not all Python scripts are suitable for an interactive session. This will be demonstrated by two Python example scripts.
Our first example Python script is called sum-2args.py: it is a simple script that adds two numbers from command-line arguments:
import sys
x = int(sys.argv[1])
y = int(sys.argv[2])
sum = x + y
print("The sum of the two numbers is: {0}".format(sum))
Our second example Python script is called add2.py: it is a simple script that adds two numbers from user input:
# This program will add two numbers that are provided by the user
# Get the numbers
a = int(input("Enter the first number: "))
b = int(input("Enter the second number: "))
# Add the two numbers together
sum = a + b
# Output the sum
print("The sum of {0} and {1} is {2}".format(a, b, sum))
Exercise
Why is/is it not a good script for interactive?
Exercises
- Go to the program directory in your cloned HPC-Python repository
cd <path-to-your-area-under-the-storage-dir>/HPC-python/Exercises/examples/programs
There you’ll find the two programs that we will use:
sum-2args.pyandadd2.py
After loading a Python module (potentially with prerequisites), run the two programs.
python sum-2args.py 3 14
python add2.py
Add numbers according to prompts.
If this works you are good to go for the interactive session exercises!
Exercise 1: start an interactive session
In this example we will start a session with 2 cores
On UPPMAX, interactive is recommended:
interactive -A naiss2024-22-1442 -p core -n 2
salloc -A hpc2n2024-142 -n 2 -t 00:30:00
interactive -A lu2024-2-88 -t 00:30:00 -n 2
interactive -A naiss2024-22-1493 -n 2
Exercise 2: check to be in an interactive session
Use:
hostname
Use:
srun hostname
Misleading would be to use:
hostname
This will always show that you are on a login node
Exercise 3: check to have booked the expected amount of cores
Confirm to have booked two cores.
Use:
srun hostname
Use:
srun hostname
Exercise 4.1. Running the first Python script in an interactive session on all cores
Running sum-2args.py in an interactive session
HPC2N, UPPMAX, LUNARC, and NSC
Run the script using srun:
b-an01 [~]$ srun python sum-2args.py 3 4 The sum of the two numbers is: 7 The sum of the two numbers is: 7 b-an01 [~]$
Similar to srun hostname, this script is run once per node and works as expected.
Exercise 4.2. Running a second Python script in an interactive session on all cores
Running add2.py in an interactive session
HPC2N, UPPMAX, LUNARC, NSC
Run the script using srun:
b-an01 [~]$ srun python add2.py
2
3
Enter the first number: Enter the second number: The sum of 2 and 3 is 5
Enter the first number: Enter the second number: The sum of 2 and 3 is 5
As you can see, it is possible, but it will not show any interaction it otherwise would have. At least not at HPC2N. Is it different elsewhere?
Exercise 5: exit
Exit the interactive mode
Use:
exit
The prompt should change to contain the name of the login node (contain rackham, cosmos, or tetralith), which indicates you are back on a login node.
Use:
exit
The prompt will remain the same.
Conclusion
Keypoints
You have:
seen how to use a compute node interactively, which differs between HPC2N, UPPMAX, LUNARC, and NSC (particularly between HPC2N and the others)
checked if we are in an interactive session
checked if we have booked the right number of cores
run Python scripts in an interactive session, which differs between HPC2N and the others
seen that not all Python scripts can be run interactively on multiples cores
exited an interactive session