Running Python in batch mode
Questions
What are the UPPMAX and HPC2N clusters?
What is a batch job?
How to make a batch job?
Objectives
Short overview of the HPC systems
Short introduction to SLURM scheduler
Show structure of a batch script
Try example
Briefly about the cluster hardware and system at UPPMAX and HPC2N
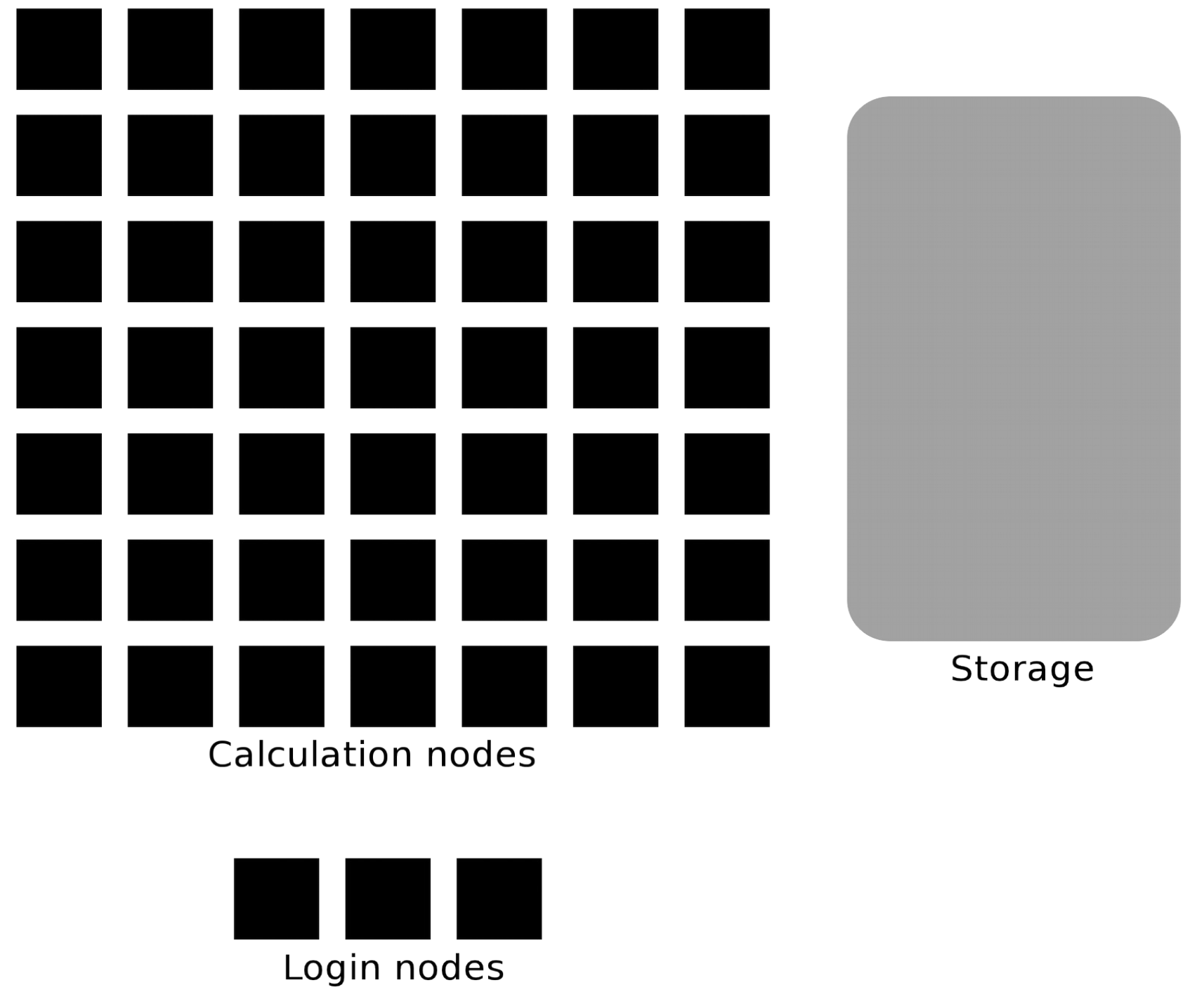
What is a cluster?
Login nodes and calculations/compute nodes
A network of computers, each computer working as a node.
Each node contains several processor cores and RAM and a local disk called scratch.
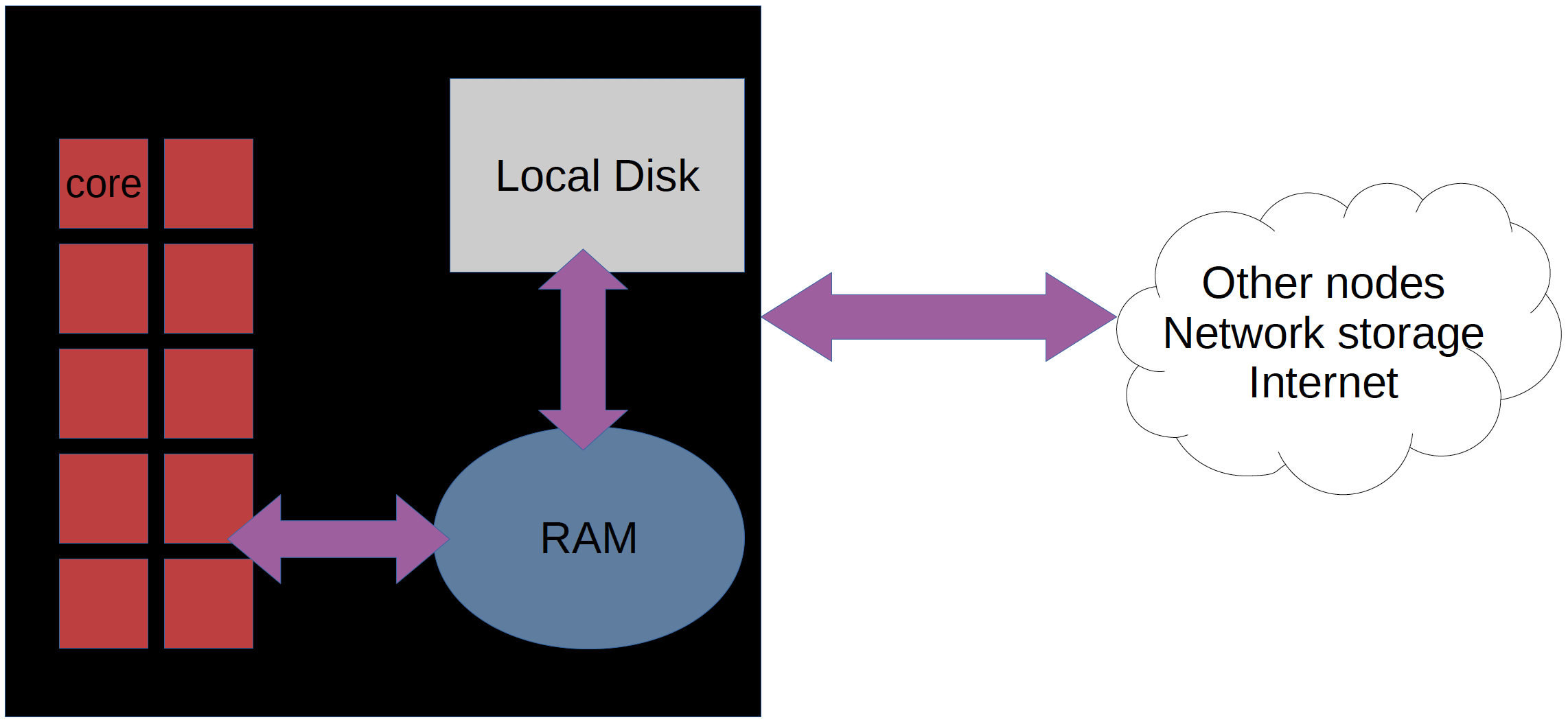
The user logs in to login nodes via Internet through ssh or Thinlinc.
Here the file management and lighter data analysis can be performed.
The calculation nodes have to be used for intense computing.
Beginner’s guide to clusters: https://www.hpc2n.umu.se/documentation/guides/beginner-guide
Common features
Intel CPUs
Linux kernel
Bash shell
Technology |
Kebnekaise |
Rackham |
Snowy |
Bianca |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cores per calculation node |
28 (72 for largemem part + 8 nodes with 128) |
20 |
16 |
16 |
Memory per calculation node |
128-3072 GB |
128-1024 GB |
128-4096 GB |
128-512 GB |
GPU |
NVidia V100 + 3 NVidia A100, |
None |
Nvidia T4 |
2 NVIDIA A100 |
Running your programs and scripts on UPPMAX and HPC2N
Any longer, resource-intensive, or parallel jobs must be run through a batch script.
The batch system used at both UPPMAX and HPC2N is called SLURM.
SLURM is an Open Source job scheduler, which provides three key functions
Keeps track of available system resources
Enforces local system resource usage and job scheduling policies
Manages a job queue, distributing work across resources according to policies
In order to run a batch job, you need to create and submit a SLURM submit file (also called a batch submit file, a batch script, or a job script).
Guides and documentation at: http://www.hpc2n.umu.se/support and http://docs.uppmax.uu.se/cluster_guides/slurm/
Workflow
Write a batch script
Inside the batch script you need to load the modules you need (Python, Python packages, any prerequisites, … )
Possibly activate an isolated/virtual environment to access own-installed packages
Ask for resources depending on if it is a parallel job or a serial job, if you need GPUs or not, etc.
Give the command(s) to your Python script
Submit batch script with
sbatch <my-python-script.sh>
Common file extensions for batch scripts are .sh or .batch, but they are not necessary. You can choose any name that makes sense to you.
Useful commands to the batch system
Submit job:
sbatch <jobscript.sh>Get list of your jobs:
squeue -u <username>Check on a specific job:
scontrol show job <job-id>Delete a specific job:
scancel <job-id>Useful info about a job:
sacct -l -j <job-id> | less -SUrl to a page with info about the job (Kebnekaise only):
job-usage <job-id>
Example Python batch scripts
Serial code
Hint
Type along!
This first example shows how to run a short, serial script. The batch script (named run_mmmult.sh) can be found in the directory /HPC-Python/Exercises/examples/<center>, where <center> is hpc2n or uppmax. The Python script is in /HPC-Python/Exercises/examples/programs and is named mmmult.py.
The batch script is run with
sbatch run_mmmult.sh.Try type
squeue -u <username>to see if it is pending or running.When it has run, look at the output with
nano slurm-<jobid>.out.
Short serial example script for Rackham. Loading Python 3.11.8. Numpy is preinstalled and does not need to be loaded.
#!/bin/bash -l
#SBATCH -A naiss2024-22-415 # Change to your own after the course
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # Asking for 10 minutes
#SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core
# Load any modules you need, here Python 3.11.8.
module load python/3.11.8
# Run your Python script
python mmmult.py
Short serial example for running on Kebnekaise. Loading SciPy-bundle/2023.07 and Python/3.11.3
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -A hpc2n2024-052 # Change to your own
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # Asking for 10 minutes
#SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core
# Load any modules you need, here for Python/3.11.3 and compatible SciPy-bundle
module load GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3 SciPy-bundle/2023.07
# Run your Python script
python mmmult.py
Python example code
import timeit
import numpy as np
starttime = timeit.default_timer()
np.random.seed(1701)
A = np.random.randint(-1000, 1000, size=(8,4))
B = np.random.randint(-1000, 1000, size =(4,4))
print("This is matrix A:\n", A)
print("The shape of matrix A is ", A.shape)
print()
print("This is matrix B:\n", B)
print("The shape of matrix B is ", B.shape)
print()
print("Doing matrix-matrix multiplication...")
print()
C = np.matmul(A, B)
print("The product of matrices A and B is:\n", C)
print("The shape of the resulting matrix is ", C.shape)
print()
print("Time elapsed for generating matrices and multiplying them is ", timeit.default_timer() - starttime)
Serial code + self-installed package in virt. env.
Hint
Don’t type along! We will go through an example like this with your self-installed virtual environment under the ML section.
Short serial example for running on Rackham. Loading python/3.11.8 + using any Python packages you have installed yourself with venv.
#!/bin/bash -l
#SBATCH -A naiss2024-22-415 # Change to your own after the course
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # Asking for 10 minutes
#SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core
# Load any modules you need, here for python 3.11.8
module load python/3.11.8
# Activate your virtual environment.
source /proj/hpc-python/<user-dir>/<path-to-virtenv>/<virtenv>/bin/activate
# Run your Python script (remember to add the path to it
# or change to the directory with it first)
python <my_program.py>
Short serial example for running on Kebnekaise. Loading SciPy-bundle/2023.07, Python/3.11.3, matplotlib/3.7.2 + using any Python packages you have installed yourself with virtual environment.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -A hpc2n2024-052 # Change to your own
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # Asking for 10 minutes
#SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core
# Load any modules you need, here for Python/3.11.3 and compatible SciPy-bundle
module load GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3 SciPy-bundle/2023.07 matplotlib/3.7.2
# Activate your virtual environment.
source /proj/nobackup/python-hpc/<user-dir>/<path-to-virt-env>/bin/activate
# Run your Python script (remember to add the path to it
# or change to the directory with it first)
python <my_program.py>
Job arrays
This is a very simple example of how to run a Python script with a job array.
Hint
Do not type along! You can try it later during exercise time if you want!
# import sys library (we need this for the command line args)
import sys
# print task number
print('Hello world! from task number: ', sys.argv[1])
#!/bin/bash -l
# This is a very simple example of how to run a Python script with a job array
#SBATCH -A naiss2024-22-415 # Change to your own after the course
#SBATCH --time=00:05:00 # Asking for 5 minutes
#SBATCH --array=1-10 # how many tasks in the array
#SBATCH -c 1 # Asking for 1 core # one core per task
#SBATCH -o hello-world-%j-%a.out
# Set a path where the example programs are installed.
# Change the below to your own path to where you placed the example programs
MYPATH=/proj/hpc-python/<userdir>/HPC-python/Exercises/examples/programs/
# Load any modules you need, here for Python 3.11.8
ml uppmax
ml python/3.11.8
# Run your Python script
srun python $MYPATH/hello-world-array.py $SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID
#!/bin/bash
# This is a very simple example of how to run a Python script with a job array
#SBATCH -A hpc2n2024-052 # Change to your own!
#SBATCH --time=00:05:00 # Asking for 5 minutes
#SBATCH --array=1-10 # how many tasks in the array
#SBATCH -c 1 # Asking for 1 core # one core per task
#SBATCH -o hello-world-%j-%a.out
# Set a path where the example programs are installed.
# Change the below to your own path to where you placed the example programs
MYPATH=/proj/nobackup/python-hpc/<your-dir>/HPC-python/Exercises/examples/programs/
# Load any modules you need, here for Python 3.11.3
ml GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3
# Run your Python script
srun python $MYPATH/hello-world-array.py $SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID
GPU code
Hint
Type along!
Short GPU example for running compute.py on Snowy.
#!/bin/bash -l
#SBATCH -A naiss2024-22-415
#SBATCH -t 00:10:00
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH -M snowy
#SBATCH --gres=gpu=1
# Load any modules you need, here loading python 3.11.8 and the ML packages
module load uppmax
module load python/3.11.8
module load python_ML_packages/3.11.8-gpu
# Run your code
python compute.py
Example with running compute.py on Kebnekaise.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -A hpc2n2024-052 # Change to your own
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # Asking for 10 minutes
# Asking for one V100 card
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:v100:1
# Remove any loaded modules and load the ones we need
module purge > /dev/null 2>&1
module load GCC/12.3.0 OpenMPI/4.1.5 Python/3.11.3 SciPy-bundle/2023.07 numba/0.58.1
# Run your Python script
python compute.py
This Python script can (just like the batch scripts for UPPMAX and HPC2N), be found in the /HPC-Python/Exercises/examples directory, under the subdirectory programs - if you have cloned the repo or copied the tarball with the exercises.
from numba import jit, cuda
import numpy as np
# to measure exec time
from timeit import default_timer as timer
# normal function to run on cpu
def func a):
for i in range(10000000):
a[i]+= 1
# function optimized to run on gpu
@jit(target_backend='cuda')
def func2(a):
for i in range(10000000):
a[i]+= 1
if __name__=="__main__":
n = 10000000
a = np.ones(n, dtype = np.float64)
start = timer()
func(a)
print("without GPU:", timer()-start)
start = timer()
func2(a)
print("with GPU:", timer()-start)
Exercises
Run the first serial example script from further up on the page for this short Python code (sum-2args.py)
import sys
x = int(sys.argv[1])
y = int(sys.argv[2])
sum = x + y
print("The sum of the two numbers is: {0}".format(sum))
Remember to give the two arguments to the program in the batch script.
Solution for HPC2N
This batch script is for Kebnekaise. Adding the numbers 2 and 3.
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH -A hpc2n2024-052 # Change to your own #SBATCH --time=00:05:00 # Asking for 5 minutes #SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core # Load any modules you need, here for Python 3.11.3 module load GCC/12.3.0 Python/3.11.3 # Run your Python script python sum-2args.py 2 3
Solution for UPPMAX
This batch script is for UPPMAX. Adding the numbers 2 and 3.
#!/bin/bash -l #SBATCH -A naiss2024-22-415 # Change to your own after the course #SBATCH --time=00:05:00 # Asking for 5 minutes #SBATCH -n 1 # Asking for 1 core # Load any modules you need, here for python 3.11.8 module load python/3.11.8 # Run your Python script python sum-2args.py 2 3
Keypoints
The SLURM scheduler handles allocations to the calculation nodes
Interactive sessions was presented in last slide
Batch jobs runs without interaction with user
A batch script consists of a part with SLURM parameters describing the allocation and a second part describing the actual work within the job, for instance one or several Python scripts.
Remember to include possible input arguments to the Python script in the batch script.