Introduction to Slurm¶
Learning outcomes
- Reach compute nodes (Hands-on A & B)
- Know when interactive vs batch (Decision + Scenario Quiz)
- Run interactively (Hands-on A)
- Run simple jobs (Hands-on B)
- Plan jobs (Efficiency & Core-hours + mini exercise)
- Check progress (Monitoring & Cancellation)
- Use documentation (Links + encourage quick look-ups during tasks)
Notes for teachers
Teaching goals:
- The learners demonstrate to have run in interactive
- The learners demonstrate to have run batch job
- The learners demonstrate to have understood when to use batch or interactive
- The learners demonstrate to have understood how to plan for jobs
Schedule (50 minutes):
- 10 minutes: lecturing
- 5 minutes type-alongs ??
- 20 minutes: exercise + quiz
- 5 minutes: discuss answers
What & Why¶
- You are already on the login node. Heavy work must run on compute nodes.
- Slurm books (reserves) cores + time for you so jobs from many researchers can share the cluster fairly.
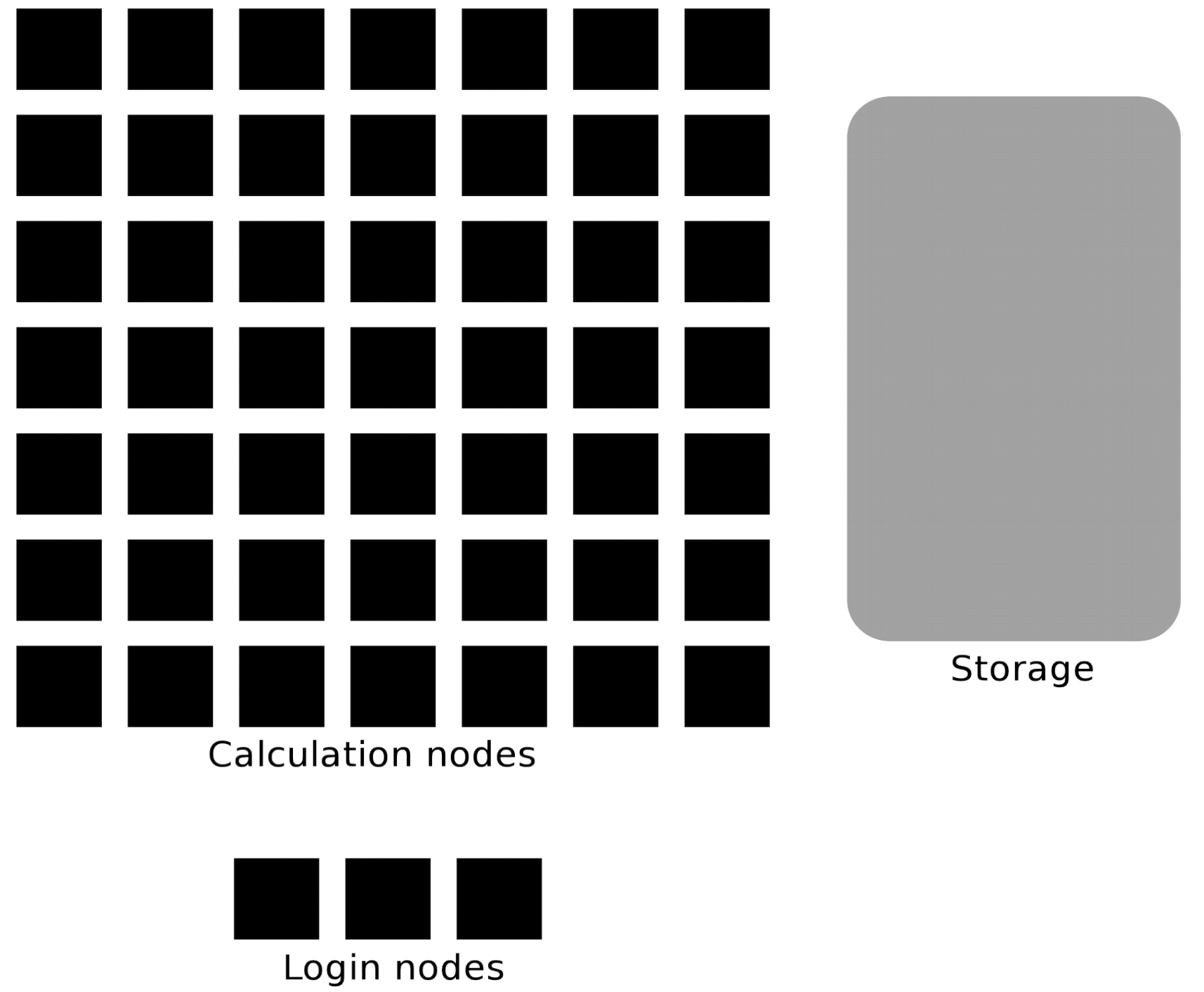
Mental Model: Hardware¶
- Login node: lightweight command & submission point (do not run heavy jobs here)
- Compute nodes: where your jobs actually run
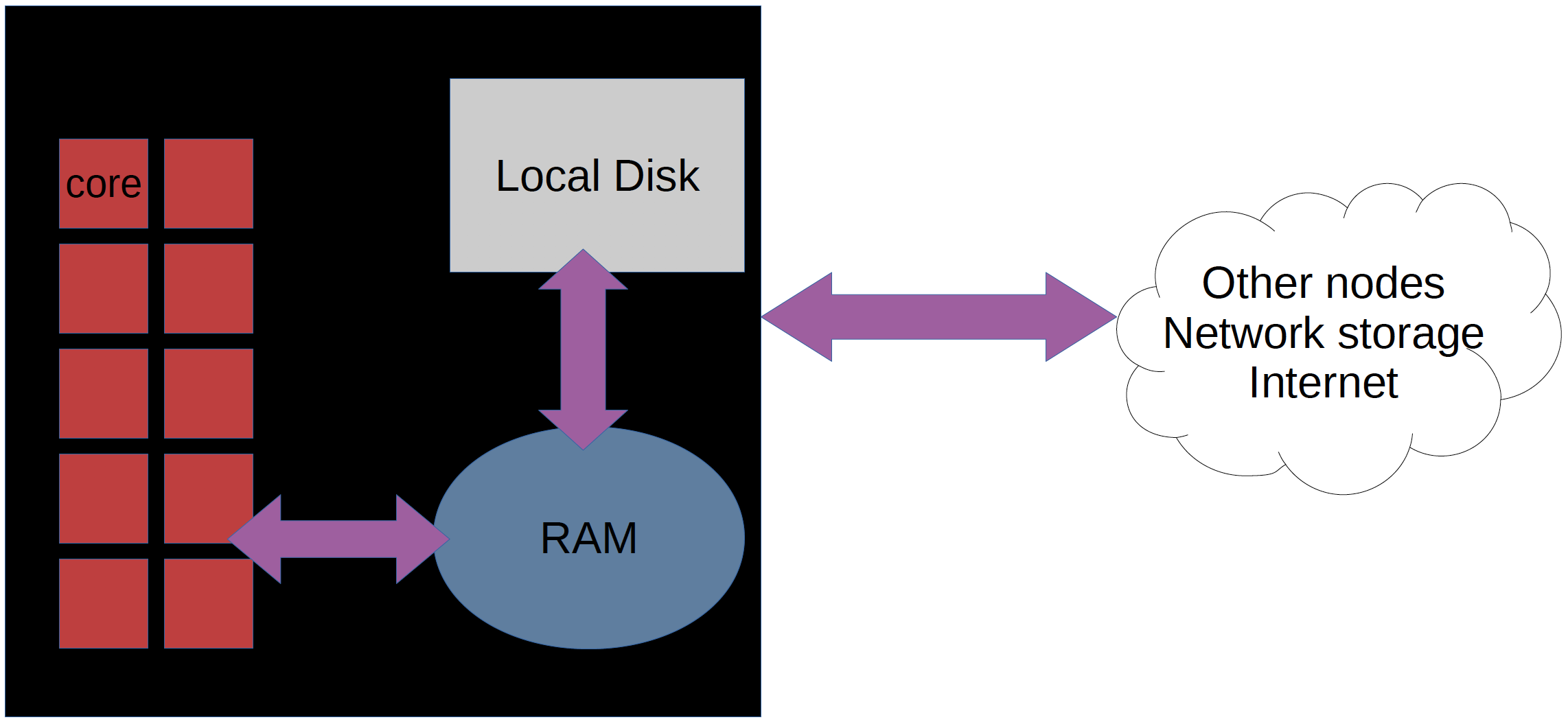
- Node: a physical machine; Core: one processing unit within a node
- NEWS!: More 256 GB memory nodes (
-C mem256GB) and login nodes memory increased from 15->30GB
Glossary (quick): Node, Core, Partition, Job, Wall time, Core-hours.
Core concepts¶
- Interactive session = temporary shell on a compute node (fast feedback)
- Batch job = script submitted; runs unattended; releases resources when done
- Resource request = (project, partition, cores, wall time)
- Core-hours = cores x (actual runtime)
Decide: Interactive or Batch¶
Decision maker
flowchart TD
UPPMAX(What to run on which node?)
operation_type{What type of operation/calculation?}
interaction_type{Need live tweaking or GUI?}
login_node(Work on login node)
interactive_node(Interactive session)
calculation_node(Batch Job)
UPPMAX-->operation_type
operation_type-->|light,short|login_node
operation_type-->|heavy,long|interaction_type
interaction_type-->|Yes|interactive_node
interaction_type-->|No|calculation_nodeRule of thumb:
- Development / GUI / rapid loop / plotting => Interactive
- Long, unattended, repeats, many samples => Batch
- Many short independent tasks => Batch (later: arrays)
Minimal Commands¶
| Action | Command (example) |
|---|---|
| Interactive session | interactive -A sens2025560 -p core -n 1 -t 00:10:00 |
| Submit batch | sbatch job.sh |
| List my in-queue jobs | squeue --me or jobinfo |
| Cancel a job | scancel <jobid> |
| Override cores/time | sbatch -n 2 -t 00:05:00 job.sh |
Keep modules: load them INSIDE the interactive session or inside the batch script.
Hands-on A: Interactive¶
-
Start:
(If waiting PENDING: observe later with
squeue --meorjobinfo.) -
Inside node:
-
Confirm you are back on login node (
hostnamechanges).
Hands-on B: First Batch Job¶
Create file hello_job.sh:
#!/bin/bash -l
#SBATCH -A sens2025560
#SBATCH -p core
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH -t 00:02:00
#SBATCH -J hello
#SBATCH -o hello_%j.out
echo "Node: $(hostname)"
date
sleep 15
echo "Done."
Submit:
After it finishes:
Try a re-submit with 2 cores overriding script:
(Add an srun hostname line to see per-task output.)
Monitoring & Cancellation¶
squeue --me: Your waiting jobs. Look at ST (R=running, PD=pending)jobinfo: All your running and waiting jobs.bianca_combined_jobinfo: All the running and waiting jobs on Bianca- Reasons (e.g. ReqNodeNotAvail, JobArrayTaskLimit, Resources)
- Cancel (demo):
scancel <jobid> - Output files pattern: defined with
-oor defaultslurm-<jobid>.out
Efficiency & Core-hours¶
Formula: core-hours = cores x (requested time if job runs full time; charged up to what you reserve).
Examples:
- 1 core x 2 h = 2 core-h
- 8 cores x 0.5 h = 4 core-h
Interactive idle problem: reserving 4 cores for 8 h but active use 1 h ⇒ charged 32 vs useful 4 core-h.
Mini Exercise: Choose minimal sufficient request for a script expected to run 12 min on 1 core:
- Bad:
-n 4 -t 02:00:00(too much resources requested) - Good:
-n 1 -t 00:20:00(book twice the hours)
Scenario Quiz¶
Decide Interactive or Batch + minimal flags:
- 6 h genome alignment (no interaction)
- Rapid R plotting tuning (needs live edits)
- 200 independent 1 min QC runs
- GUI RStudio exploratory stats (≤4 h)
- Pipeline already validated (repeat weekly)
(Join at menti.com | code 5863 8668)
Cheat Sheet¶
-Aproject-ppartition (devcore/develfor small tests,coregeneral,nodewhole node)-ncores-Nnodes-twall time (HH:MM:SS or D-HH:MM:SS) Optional (read later):-Jjob name-ooutput filename--mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL-C mem256GB(fat node),-C gpu,--gpus-per-node 1
Reminders¶
- Keep data/outputs in
/proj/sens2025560/...not only$HOMEor wharf. - No external data pulls mid-job. Bianca is cut-off from internet.
- Job walltime limit for batch job is 10 days and for interactive session is 12 hrs.
EXTRA: Advanced Workflow (Optional)¶
-
Make a batch job to run the "Hands on: Processing a BAM file to a VCF using GATK, and annotating the variants with snpEff" demo. Ask for 2 cores for 1h.
-
You can copy the
my_bio_workflow.shfile in/proj/sens2025560/workshop/slurmto your home folder and make the necessary changes.Answer
- edit a file using you preferred editor, named
my_bio_worksflow.sh, for example, with the content -
alternatively copy the
/proj/sens2025560/workshop/slurm/my_bio_workflow.shfile and modify itcd ~cp /proj/sens2025560/workshop/slurm/my_bio_workflow.sh .
-
edit
my_bio_workflow.shand add the SBATCH commands
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH -A sens2025560 #SBATCH -J workflow #SBATCH -t 01:00:00 #SBATCH -p core #SBATCH -n 2 cd ~ mkdir -p myworkflow cd myworkflow module load bioinfo-tools # load samtools module load samtools/1.17 # copy and example BAM file cp -a /proj/sens2025560/workshop/data/Col0_C1.100k.bam . # index the BAM file samtools index Col0_C1.100k.bam # load the GATK module module load GATK/4.3.0.0 # make symbolic links to the hg38 genomes ln -s /sw/data/iGenomes/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.* . # create a VCF containing inferred variants gatk HaplotypeCaller --reference genome.fa --input Col0_C1.100k.bam --intervals chr1:100300000-100800000 --output Col0_C1.100k.vcf # use snpEFF to annotate variants module load snpEff/5.1 java -jar $SNPEFF_ROOT/snpEff.jar eff hg38 Col0_C1.100k.vcf > Col0_C1.100k.snpEff.vcf # compress the annotated VCF and index it bgzip Col0_C1.100k.snpEff.vcf tabix -p vcf Col0_C1.100k.snpEff.vcf.gz- make the job script executable
- submit the job
- edit a file using you preferred editor, named
Optional (Self-Study)¶
- RStudio in an interactive session
- Advanced bioinformatics workflow (GATK + snpEff)
- Efficient multi-core & job arrays (see extra material: replicate jobs)
- Monitoring resource usage:
jobstats(see intermediate: efficient jobs)
Links¶
- New Slurm user guide
- Discovering job resource usage with
jobstats - Plotting your core hour usage
- The job scheduler graphically
- Official slurm documentation
FAQs¶
Why -l
- It is good practice to end the line with
-lto reload a fresh environment with no modules loaded. - This makes you sure that you don't enable other software or versions that may interfere with what you want to do in the job.
Why initial#
#will be ignored bybashand can run as an ordinary bash script- If running the script with the command
sbatch <script>the#SBATCHlines will be interpreted as slurm flags
How many cores in a compute/login node?
- On a compute node, there are 16 cores in one node. But effectively, you can use only 15 cores of a node.
- On a login node, there are 2 cores which are shared among all the project members.
How much memory in a compute/login node?
- On a compute node, you have 128, 256, 512 GB variants. By default, you get 128 GB unless you specify using
-Cflag, like-C mem256GB - On a login node, you have 16GB memory only.
Do you have GPUs?
- Bianca has 10 nodes with 2xA100 40GB GPUs per node.
- Use
-C gpuflag to request a gpu node. Use-C gpu --gpus_per_node=1if you only want to use one. - GPU nodes have 256 GB memory.
What is the maximum limit my job can run for?
- Job walltime for a job on interactive session is limited to 12 hrs and on compute node to 10 days.
- Send us a ticket, with justification, via Supr if you like to extend your job beyond this limit.